|
Cosmetic breast surgery
Definition
Breast augmentation is a procedure to change the size or shape of the breasts.
See also:
Alternative Names
Breast augmentation; Breast implants; Implants - breast; Mammaplasty
Description
Cosmetic breast surgery may be done at an outpatient surgery clinic or in a hospital.
- Most women receive general anesthesia for this surgery. You will be asleep and pain-free.
- You may also be given medicine to relax you and local anesthesia. You will be awake and will receive medicine to numb your breast area to block pain.
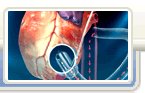
There are many different ways to place breast implants:
- In the most common technique, the surgeon will make surgical cut on the underside of your breast, in the natural skin fold. Your surgeon will place the implant through this opening. Your scar may be a little more visible if you are younger, thin, and have not yet had children.
- The implant may be placed through a surgical cut under your arm. Your surgeon may perform this surgery using an endoscope (a tool with a camera and surgical instruments at the end that is inserted through a vein). There will be no scar around your breast, but you may have a visible scar on the underside of your arm.
- The surgeon may make a cut around the edge of your areola, the darkened area around your nipple. The implant is placed through this opening. You may have more problems with breastfeeding and loss of sensation around your nipple with this method.
- A newer technique involves placing a saline implant through a surgical cut near your belly button. An endoscope is used to move the implant up to the breast area. Once in place, the implant is filled with saline.
Breast implants may be placed either directly behind the breast tissue (subglandular) or behind the outer layer of chest wall muscles (submuscular). The type of implant and implant surgery can affect:
- How much pain you have after the procedure
- The appearance of your breast
- The risk of the implant breaking or leaking in the future
- Your future mammograms
Your surgeon can help you decide which procedure is best for you.
|
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Breast augmentation is done to increase the size of your breasts.
A breast lift, or mastopexy, is usually done to lift sagging, loose breasts. The size of the areola, the dark pink skin surrounding the nipple, can also be reduced.
Talk with a plastic surgeon if you are considering cosmetic breast surgery. Discuss how you expect to look and feel better. Keep in mind the desired result is improvement, not perfection. Emotional stability is an important factor. Breast surgery can renew your self-confidence and improve your appearance, but the rest is up to you.
Risks
Risks for any surgery are:
- Bleeding
- Infection
Risks for any anesthesia are:
- Reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems, pneumonia
- Heart problems
Risks for breast surgery are:
- Difficulty breastfeeding
- Loss of feeling in the nipple area
- Small scars, usually in an area where they do not show much. Some women may have thickened, raised scars.
- Uneven position of your nipples
- Different size or shape of the two breasts
- It is normal for your body to create a “capsule” made up of scar tissue around your new breast implant. This helps keep the implant in place. Sometimes, this capsule becomes thickened and larger and may cause a change in the shape of your breast, hardening of breast tissue, or some pain.
- Breaking or leakage of the implant
- Visible rippling of the implant
The emotional risks of surgery may include feeling that your breasts don't look perfect, or you may be disappointed with people's reactions to your “new” breasts.
Before the Procedure
Always tell your doctor or nurse:
- If you are or could be pregnant
- What drugs you are taking, even drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription
During the days before your surgery:
- You may need mammograms or breast x-rays before surgery. Your plastic surgeon will do a routine breast exam.
- Several days before surgery, you may be asked to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), warfarin (Coumadin), and any other drugs that make it hard for your blood to clot.
- Ask your doctor which drugs you should still take on the day of surgery.
- You may need to fill prescriptions for pain medicine before surgery.
- Arrange for someone to drive you home after surgery and help you around the house for 1 or 2 a days.
- If you smoke, try to stop. Ask your doctor or nurse for help.
On the day of the surgery:
- You will usually be asked not to drink or eat anything after midnight the night before surgery.
- Take the drugs your doctor told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Wear or bring loose clothing that buttons or zips in front and a soft, loose-fitting bra with no underwire.
- Your doctor or nurse will tell you when to arrive at the hospital.
After the Procedure
You may need to stay overnight in the hospital. Some women can go home when their anesthesia wears off and they can walk, drink water, get to the bathroom safely, and have pain they can manage at home.
After breast augmentation surgery, a bulky gauze dressing will be wrapped around your breasts and chest, or you might wear a surgical bra. Drainage tubes may be attached to your breasts. These will be removed within 3 days.
Sometimes doctors also recommend massaging the breast starting 5 days after surgery to reduce hardening of the capsule that surrounds the implant. Ask your doctor first before massaging over your implants.
Outlook (Prognosis)
You are likely to have a very good outcome from breast surgery. You may feel better about your appearance and yourself. Also, the pain or skin symptoms you had (such as striation) will disappear. You may need to wear a special supportive bra for a few months to reshape your breasts.
Scars are permanent and are often more visible in the year after surgery. They will fade after this. Your surgeon will try to place the incisions so that your scars are as hidden as possible. Your scars should not be noticeable, even in low-cut clothing, since incisions are usually made on the underside of the breast.
References
Burns JL, Blackwell SJ. Plastic surgery. In: Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2008:chap 73.
Sarwer DB. The psychological aspects of cosmetic breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007 Dec;120(7 Suppl 1):110S-117S.
Hölmich LR, Lipworth L, McLaughlin JK, Friis S. Breast implant rupture and connective tissue disease: a review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007 Dec;120(7 Suppl 1):62S-69S.
McLaughlin JK, Lipworth L, Fryzek JP, Ye W, Tarone RE, Nyren O. Long-term cancer risk among Swedish women with cosmetic breast implants: an update of a nationwide study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Apr 19;98(8):557-60.
Wiener TC. Relationship of incision choice to capsular contracture. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2008 Mar;32(2):303-6.
Reviewed By: David A. Lickstein, MD, FACS, specializing in cosmetic and reconstructive plastic surgery, Palm Beach Gardnes, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.